基本信息

毛新愿 男 中国科学院空间应用工程与技术中心
电子邮件: maoxinyuan@csu.ac.cn
通信地址: 北京市海淀区邓庄南路9号 (邮编:100094)
邮政编码:
电子邮件: maoxinyuan@csu.ac.cn
通信地址: 北京市海淀区邓庄南路9号 (邮编:100094)
邮政编码:
研究领域
研究领域一:低轨卫星精密定轨
低地球轨道是人类航天最频繁使用的卫星轨道。为实现研究目标,地球科学、对地遥感、气象研究等卫星或星座往往需要尽可能好的轨道,提出了高精度绝对和相对精密定轨的需求。利用星载GPS/北斗技术,可实现绝对定轨1-2厘米级、相对定轨1毫米级的精度。
- 针对复杂外型的卫星,需研究精细的动力学模型,尤其是非保守力(太阳光压、空气动力、地球反照压/辐射压)
- 针对串联型、钟摆型、高动态型、跨任务型卫星编队,需设计对应的精密定轨方案。
- 针对天宫级别超大型航天器,需研究寻找质心、经验加速度补偿等综合策略。
- 针对频繁机动的低轨卫星,需研究机动建模和重估方法,以消除机动对精密定轨的影响。

上述研究内容在中国载人航天工程、欧空局(ESA)、欧洲气象卫星应用组织(EUMETSAT)、欧洲科学委员会(ERC)、瑞士国家科学基金项目(SNSF)等资助下得以验证实现,并将持续拓展。
研究领域二:地月空间航天器天基自主导航
地月空间是载人航天研究的新高地。传统地基定轨协调资源多、跟踪弧段短、精度有限,有必要研究天基自主导航方法。同时,高精度定位也意味着高精度的授时。可通过GNSS系统主瓣和旁瓣弱信号,结合天基和地基K频段测距,利用地月空间引力场不对称性,实现整个地月空间、甚至更远空间内航天器高精度自主导航。
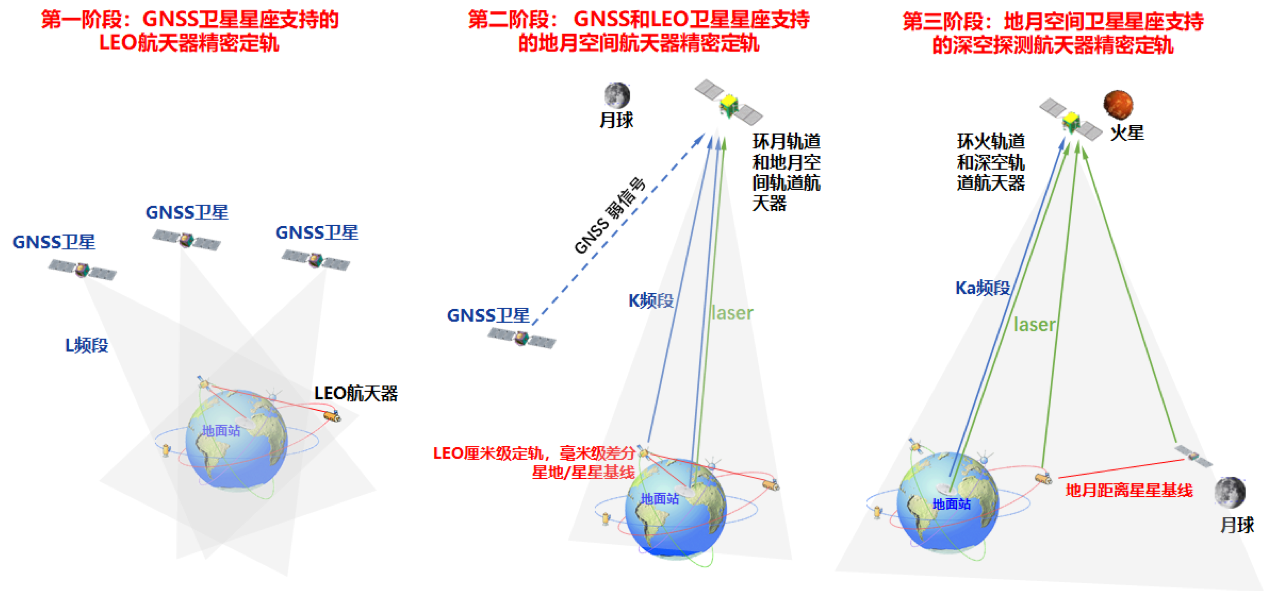
该研究内容即将在国家重大航天科研项目中验证。
招生信息
每年招硕士生1-2名
招生专业
082501-飞行器设计081105-导航、制导与控制
招生方向
卫星精密定轨,航天器轨道动力学,航天器自主导航
教育背景
2013-09--2019-06 荷兰代尔夫特理工大学航空航天学院 工学博士2010-09--2013-05 北京理工大学宇航学院 工学硕士2006-09--2010-07 北京理工大学宇航学院 工学学士
工作经历
工作简历
2023-01~现在, 中科院空间应用工程与技术中心, 副研究员2021-02~2022-12,瑞士伯尔尼大学天文研究所/欧洲卫星定轨中心, 助理研究员2019-07~2021-01,瑞士伯尔尼大学天文研究所/欧洲卫星定轨中心, 博士后2017-11~2018-12,荷兰代尔夫特理工大学航空航天学院, 研究助理
教授课程
航天器轨道确定与自主导航
出版信息
发表论文
[1] Xinyuan Mao, Daniel Arnold, Maciej Kalarus, Sebastiano Padovan, Adrian Jaggi. GNSS-based precise orbit determination for maneuvering LEO satellites. GPS Solutions[J]. 2023, 27(147): 1-11, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01494-6.[2] Mao, Xinyuan, Arnold, Daniel, Girardin, Valere, Villiger, Arturo, Jaggi, Adrian. Dynamic GPS-based LEO orbit determination with 1 cm precision using the Bernese GNSS Software. ADVANCES IN SPACE RESEARCH[J]. 2021, 67(2): 788-805, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2020.10.012.[3] da Encarnacao, Joao Teixeira, Visser, Pieter, Arnold, Daniel, Bezdek, Ales, Doornbos, Eelco, Ellmer, Matthias, Guo, Junyi, van den IJssel, Jose, Iorfida, Elisabetta, Jaggi, Adrian, Klokocnik, Jaroslav, Krauss, Sandro, Mao, Xinyuan, MayerGuerr, Torsten, Meyer, Ulrich, Sebera, Josef, Shum, C K, Zhang, Chaoyang, Zhang, Yu, Dahle, Christoph. Description of the multi-approach gravity field models from Swarm GPS data. EARTH SYSTEM SCIENCE DATA[J]. 2020, 12(2): 1385-1417, https://doaj.org/article/fdf758c9729a47cc8699af3e66211bf7.[4] Mao, Xinyuan, Visser, P N A M, van den IJssel, Jose. Absolute and relative orbit determination for the CHAMP/GRACE constellation. ADVANCES IN SPACE RESEARCH[J]. 2019, 63(12): 3816-3834, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.02.030.[5] Mao, Xinyuan, Visser, P N A M, van den Ijssel, J. High-dynamic baseline determination for the Swarm constellation. AEROSPACE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY[J]. 2019, 88: 329-339, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2019.03.031.[6] Mao, Xinyuan, Visser, P N A M, van den IJssel, J. The impact of GPS receiver modifications and ionospheric activity on Swarm baseline determination. ACTA ASTRONAUTICA[J]. 2018, 146: 399-408, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.03.009.[7] Mao, Xinyuan, Visser, P N A M, van den IJssel, J. Impact of GPS antenna phase center and code residual variation maps on orbit and baseline determination of GRACE. ADVANCES IN SPACE RESEARCH[J]. 2017, 59(12): 2987-3002, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.03.019.[8] Mao Xinyuan, Du Xiaojing, Fang Hui. Precise attitude determination strategy for spacecraft based on information fusion of attitude sensors: Gyros/GPS/Star-sensor. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AERONAUTICAL AND SPACE SCIENCES[J]. 2013, 14(1): 91-98, https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/full-record/WOS:000346989800010.[9] 张宁博, 毛新愿. 基于深空网的小天体定位方案分析. 全国深空探测年会null. 2012, [10] Mao Xinyuan, Du Xiaojing, Fang Hui. Research on Orbit Determination Strategy for LEO Based on GPS Dual-frequency Carrier Phase. 2012中国制导、导航与控制学术会议null. 2012, [11] Guo Kang, Du Xiaojing, Mao Xinyuan. Research on Multi update rate Method of Precise Satellite Attitude Determination Based on Gyro and Star-Sensor. AIAA Guidance Navigation and Control Conferencenull. 2011,
科研活动
科研项目
( 1 ) 空间站时频科学实验柜系统:精密定轨项目, 参与, 国家任务, 2019-10--2023-12( 2 ) 地月空间天基精密定轨与自主导航, 参与, 中国科学院计划, 2022-02--2027-02
参与会议
(1)Precise orbit determination for low Earth orbit satellite during maneuver periods 空间研究委员会(COSPAR)2022年科学大会 2022-07-17(2)Precise orbit determination for the maneuvering Sentinel-3 satellites 欧洲地学学会(EGU)2022年科学大会 2022-05-26(3)GPS-based dynamic orbit determination for low Earth orbit satellites 欧洲地学学会(EGU)2021年科学大会 2021-04-27(4)Impact of satellite dynamics parameterization on precise orbit determination of Sentinel-3 空间研究委员会(COSPAR)2020年科学大会 2021-02-01(5)Sentinel-3A/3B orbit determination using non-gravitational force modeling and single-receiver ambiguity resolution 欧洲地学学会(EGU)2020年科学大会 2020-05-04(6)Absolute and Relative Orbit Determination for the CHAMP-GRACE Constellation 空间研究委员会(COSPAR)2018年科学大会 2018-07-16(7)The impact of GPS receiver modifications and ionospheric activity on Swarm baseline determination 欧空局第7届Swarm卫星数据质量会议 2017-11-24(8)Impact of Swarm GPS receiver modifications on baseline determination 欧空局Swarm卫星科学会议2017 2017-03-15(9)Swarm absolute and relative orbit determination 欧空局2016年Living Planet会议 2016-05-09(10)The application of in-flight antenna pattern corrections to GPS-based baseline determination for formation flying GRACE 国际卫星编队与星座2015年会议 2015-06-08
