(一)期刊论文:#共同第一作者 *通讯作者
在ACS Nano、Small、Carbon、JPCC等国际主流期刊发表论文40多篇。
-- 2024 --
[42] Peijin Li, Anqiang Sun, CaiXia Guo, Zhilong Peng, Chao Wang*. Effects of Orientation of Myocardial Fibers on the Contractility of Left Ventricle,Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2024, Under Review;
[41] Tian Yang, Shuang Li, Yixiang Shi, Chao Wang*, Peixuan Hao*. Microscopic Deformation Mechanism of Inelasticity in Graphene Foams under Quasi-static Tension and Compression. Computational Materials Science, 2024, Accepted;
-- 2023 --
[40] Shenggui Liu, Mindong Lyu, Cheng Yang, Minqiang Jiang and Chao Wang*. Study of Viscoelastic Properties of Graphene Foams Using Dynamic Mechanical Analysis and Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Materials, 2023, 16, 2457;
[39] Bo Song, Bolin Yang, Cun Zhang, Chao Wang, Shaohua Chen*. Temperature-dependent mechanical properties and the microscopic deformation mechanism of bilayer γ-graphdiyne under tension. Nanotechnology. 2023; 34(1):015712.
[38] Muhammad Bilal Khan*, Chao Wang, Shuai Wang, Shaohua Chen b*, Strain sensitivity and microscopic deformation mechanism of graphene foam containing active nanoparticles under magnetic fields. Mechanics of Materials, 2023, 184, 104752;
[37] Shuai Wang, Chao Wang, Lihong Liang* and Shaohua Chen*, The role of graphene in Graphene-Filled carbon nanotube foam under compression and the corresponding microscopic deformation mechanism. Materials & Design, 2023, 231, 112043;
[36] Shuai Wang, Tian Yang, Chao Wang*, Lihong Liang*. The Mechanical Response and Microscopic Deformation Mechanism of Graphene Foams Tuned by Long Carbon Nanotubes and Short Crosslinkers. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2023, 25,192-202;
-- 2022 --
[35] Tianxiong Hu, Guian Qian, Xianqian Wu, Chao Wang*. Mechanical Behavior and Micro-Mechanism of Carbon Nanotube Networks under Friction. Carbon, 2022, 200(2022), 108-115;
[34] Fengxiao Chen, Jitang Fan*, David Hui, Chao Wang, Fuping Yuan, Xiaolei Wu. Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading. Nanotechnology Reviews. 2022, 11(1):3281-3291.
[33] Muhammad Bilal Khan, Chao Wang*, Shuai Wang and Shaohua Chen*. Mechanical Properties and Micro-Mechanisms of Nanoparticles-Contained Graphene Foams under Uniaxial Tension. Computational Materials Science. 2022, 206(11):111277;
[32] Yue Wu, Chao Wang* and Tian Yang. Aggregation of Nanoparticles and Their Effect on Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanotube Networks. Computational Materials Science. 2022, 202:110970;
-- 2021 --
[31] Shenggui Liu, Mindong Lyu and Chao Wang*. Mechanical Properties and Deformation Mechanisms of Graphene Foams with Bi-Modal Sheet Thickness by Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Materials. 2021, 14(19):5622;
[30] Tian Yang, Chao Wang* and Zuobing Wu*. Strain Hardening in Graphene Foams under Shear. ACS Omega. 2021, 6(35):22780-22790;
[29] Shuai Wang, Chao Wang*, Muhammad Bilal Khan and Shaohua Chen*. Microscopic Deformation Mechanism and Main Influencing Factors of Carbon Nanotube Coated Graphene Foams under Uniaxial Compression. Nanotechnology. 2021, 32(34):345704;
[28] Yifan Zhao, Yushun Zhao, Fan Wu, Yue Zhao, Yaming Wang, Chao Sui, Xiaodong He, Chao Wang*, Huifeng Tan* and Chao Wang*. The Mechanical Behavior and Collapse of Graphene-Assembled Hollow Nanospheres under Compression. Carbon. 2021, 173, 600-608;
[27] Kailu Xiao, Xudong Lei, Yuyu Chen, Qi An, Dongmei Hu, Chao Wang*, Xianqian Wu* and Chengguang Huang. Extraordinary Impact Resistance of Carbon Nanotube Film with Crosslinks under Micro-Ballistic Impact. Carbon. 2021, 175, 478-489;
[26] Muhammad Bilal Khan, Chao Wang*, Shuai Wang, Daining Fang and Shaohua Chen*. The Mechanical Property and Microscopic Deformation Mechanism of Nanoparticle-Contained Graphene Foam Materials under Uniaxial Compression. Nanotechnology. 2021, 32(11):115701;
-- 2020 --
[25] Shuai Wang, Zhilong Peng, Jianjun Li, Yazheng Yang,Chao Wang*, Shaohua Chen*. Influencing Factors of Droplet Aggregation on Hierarchical Wedge-Shaped Functional Surface. Computational Materials Science. 2020; 175:109616;
[24] Shuai Wang, Chao Wang*, Zhilong Peng, Shaohua Chen*. Spontaneous Dewetting Transition of Nanodroplets on Nanopillared Surface. Nanotechnology. 2020, 31(22):225502;
[23] Tian Yang, Chao Wang*, Zuobing Wu*. Crosslink-Tuned Large-Deformation Behavior and Fracture Mode in Buckypapers. Carbon. 2020, 159: 412-421;
[22] Muhammad Bilal Khan, Shuai Wang, Chao Wang* and Shaohua Chen*. Rotation of Nanoflake Driven by Strain Gradient Fields in Locally-Indented Graphene. Nanotechnology. 2020, 21(1):015303.
-- 2019 --
[21] Chao Wang, Cun Zhang, Shaohua Chen. The Micro-Mechanism and the Influencing Factors of Graphene Foam Elasticity. Carbon. 2019;148:267-276.
[20] Liu L, Xu ZW, Li RR, Zhu R, Xu J, Zhao JL, Chao Wang, Nordlund K, Fu X, Fang FZ. Molecular dynamics simulation of helium ion implantation into silicon and its migration. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B-beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms. 2019; 456:53-59.
[19] Shuai Wang, Chao Wang*, Zhilong Peng, Shaohua Chen*. Moving Behavior of Nanodroplets on Wedge-Shaped Functional Surfaces. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 2019; 123(3):1798-1805.
-- 2018 --
[18] Shuai Wang, Chao Wang, Zhilong Peng, Shaohua Chen. A New Technique for Nanoparticle Transport and Its Application in A Novel Nano-Sieve. Scientific Reports. 2018; 8(1):1-10.
[17] Douxing Pan, Chao Wang, Xiaojie Wang. Graphene Foam: Hole-Flake Network for Uniaxial Supercompression and Recovery Behavior. ACS Nano. 2018; 12(11):11491-11502.
[16] Feng Liu*, Chao Wang*, Qiheng Tang. Conductivity Maximum in 3D Graphene Foams. Small. 2018;1801458:1-10.
[15] Junjun Shang, Qingsheng Yang*, Xia Liu*, Chao Wang*. Compressive Deformation Mechanism of Honeycomb-like Graphene Aerogels. Carbon. 2018; 134:398-341.
[14] Chao Wang, Douxing Pan, Shaohua Chen. Energy Dissipative Mechanism of Graphene Foam Materials. Carbon. 2018;132:641-650.
-- 2017 --
[13] Douxing Pan#, Chao Wang#, Tzu-Chiang Wang,Yugui Yao. Graphene Foam:Uniaxial Tension Behavior and Fracture Mode Based on a Mesoscopic Model. ACS Nano. 2017;11(9):8988-8997.
[12] Yang Ge, Jianlong Ji, Zhizhong Shen, Qiang Zhang, Aoqun Jian, Qianqian Duan, Chao Wang, Jun jiang, Wendong Zhang, Shengbo Sang, First principles study of magnetism induced by topological frustration of bowtie-shaped graphene nanoflake. Carbon. 2017; 127(5546).
[11] Douxing Pan, Tzu-Chiang Wang, Chao Wang, Yugui Yao. Self-Assembled Chiral Phosphorus Nanotubes from Phosphorene: A Molecular Dynamics Study. RSC Advances. 2017; 7(40):24647-24651.
-- 2016 --
[10] Chao Wang, Cun Zhang, Shaohua Chen. The Microscopic Deformation Mechanism of 3D Graphene Foam Materials under Uniaxial Compression. Carbon. 2016; 109:666-672.
[9] Chao Wang, Shaohua Chen. Viscoelastic Properties of Randomly Entangled Carbon Nanotube Networks under Cyclic Tension Loading. Computational Materials Science. 2016; 119:46-51.
-- 2015 --
[8] Chao Wang, Shaohua Chen. Motion Driven by Strain Gradient Fields. Scientific Reports. 2015; 5:13675.
-- 2014 --
[7] Chao Wang, Wang LF, Xu ZP. Mechanics of Networked Materials with Dynamical Crosslinks. Comptes Rendus Mecanique. 2014; 342(5):264-72.
-- 2013 --
[6] Chao Wang, Wang LF, Xu ZP. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanotube Networks by Mobile and Discrete Binders. Carbon. 2013; 64(2013):237-44.
[5] Chao Wang, Chen SH. Application of the Complex Network Method in Solid-State Sintering. Computational Materials Science. 2013; 69:14-21.
-- 2012 --
[4] Chao Wang, Xie B, Liu YL, Xu ZP. Mechanotunable Microstructures of Carbon Nanotube Networks. ACS Macro Letters. 2012; 1(10):1176-9.
[3] Chao Wang, Chen SH. The Influence of Agglomerates on the Densification and Microstructural Evolution in Sintering of A Multi-Particle System. Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy. 2012; 55(6):1051-8.
[2] Chao Wang, Chen SH. The Effect of Agglomerate on Micro-Structural Evolution in Solid-State Sintering. Acta Mechanica Sinica. 2012; 28(5):1323-30.
[1] Chao Wang, Chen SH. Factors Influencing Particle Agglomeration During Solid-State Sintering. Acta Mechanica Sinica. 2012; 28(3):711-9.
(二)专利和软件注册权
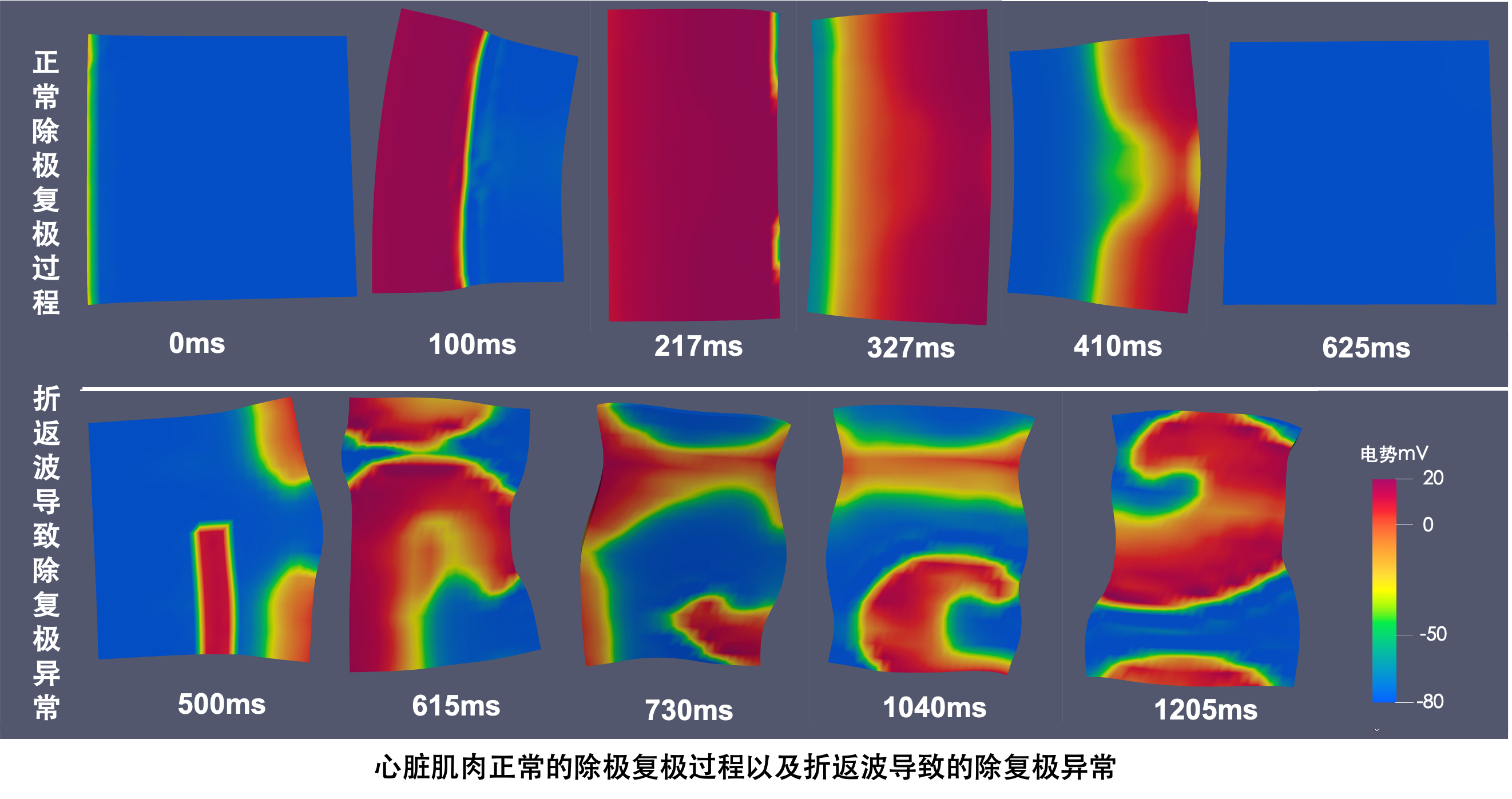
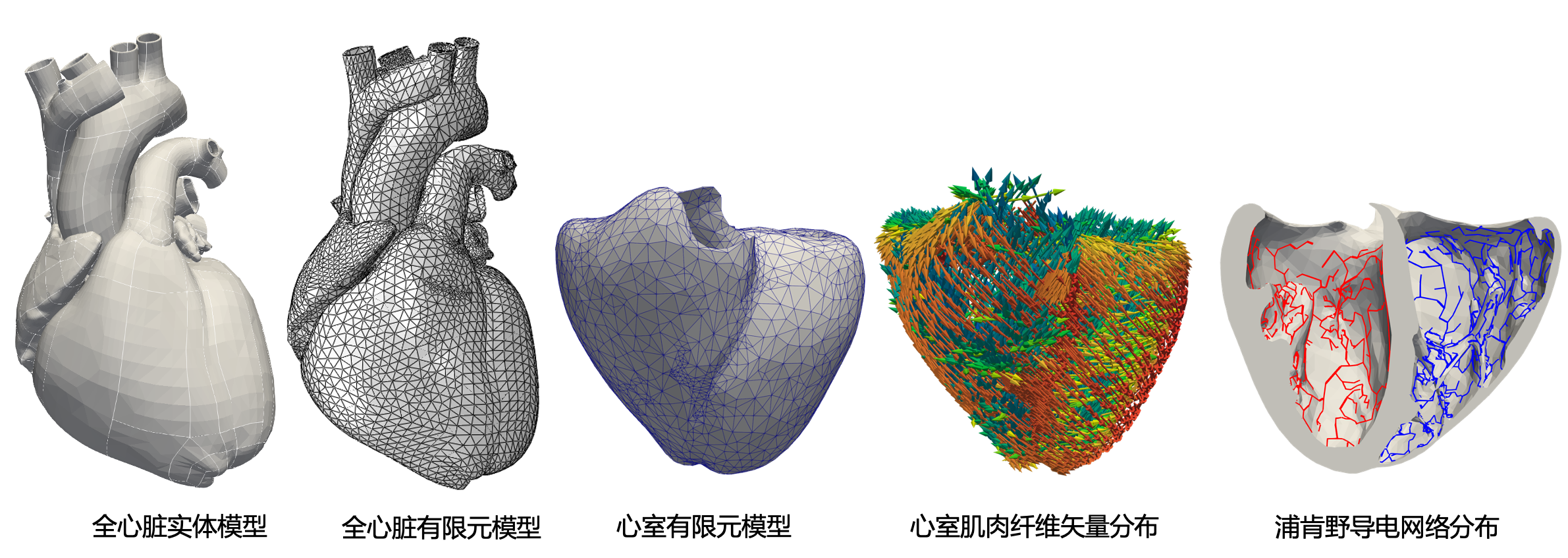
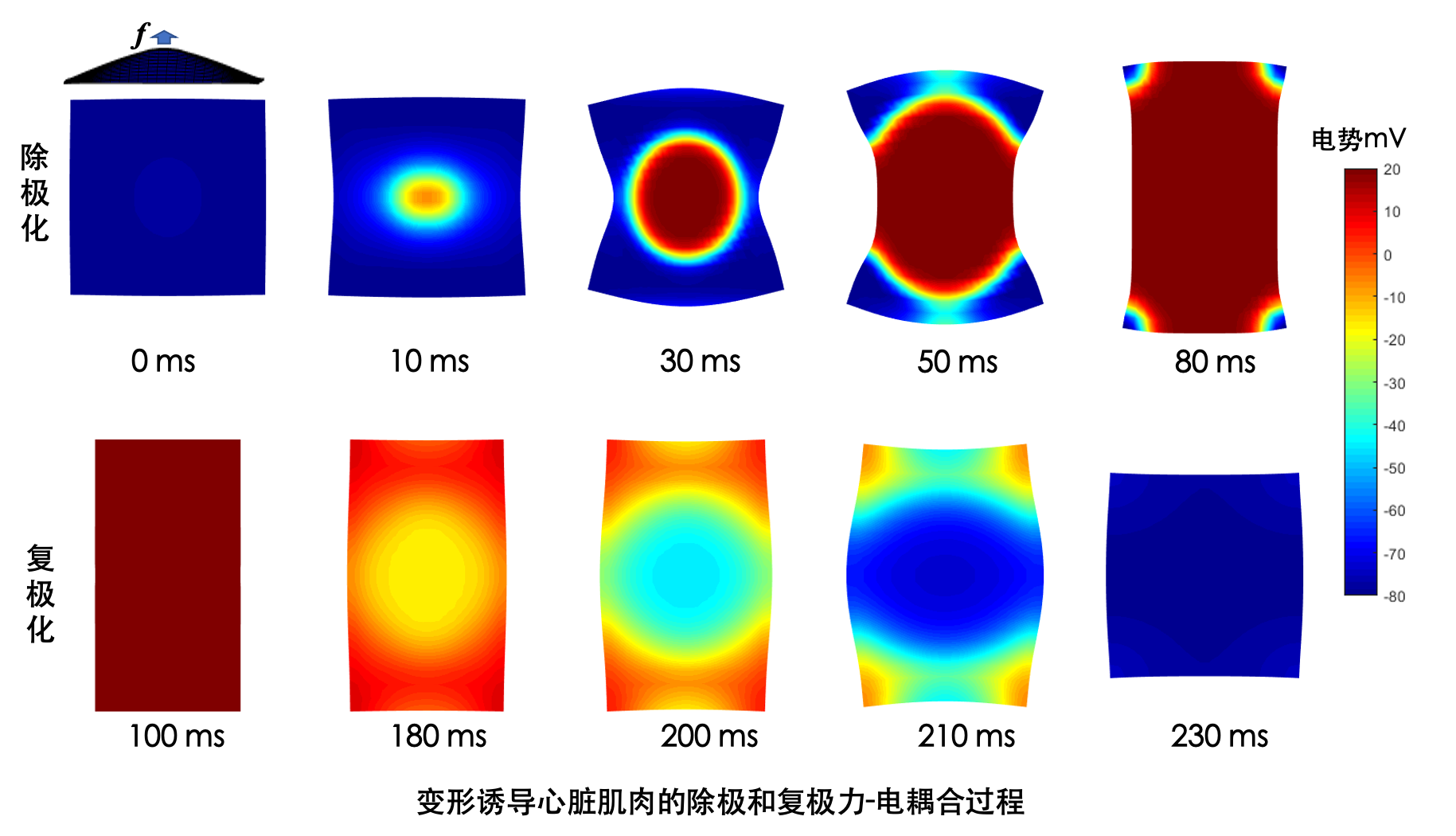
[1]王超,考虑力电耦合机理的全心脏数值模拟软件V1.0,登记号:2022SR1033830,2022.
[2]王超,利用GPU加速的全心脏数值模拟软件,登记号:2023SR0129144,2023.
[3]王超,考虑血液心肌相互作用的全心脏数值模拟软件,登记号:2024SR0103234,2024.
[4]王超,基于规则的数字心脏心肌纤维生成软件,登记号:2024SR0095794,2024.
[5]王超,一种基于非线性大变形力学原理的全心脏模拟仿真方法,专利号:202410172605.2
(三)参加会议
[7] 王超. 石墨烯泡沫材料的研究进展和研究计划. 第一届CEL研究组毕业生研讨会. 北京. 2020.12.26
[6] 王超. 石墨烯泡沫材料力电性能的微观机理研究. 固体力学青年学术沙龙. 2020.8.5
[5] 王超. 石墨烯泡沫材料弹性机理研究. 2019年中国力学大会. 杭州. 2019.8.25-28
[4] 王超,陈少华. 石墨烯泡沫材料拉压弹性机理研究. 2018全国固体力学大会. 哈尔滨. 2018.11.23-26
[3] 王超,陈少华. 惰性夹杂颗粒对固相烧结的影响. 第15届北方七省市区力学会议. 8/2014
[2] 王超,陈少华. 微颗粒烧结过程中颗粒聚团的影响因素. 中国力学大会. 7/2011
[1] 王超,陈少华. 固相烧结中颗粒团的影响(摘要). 北京力学会第十七届年会. 1/2011